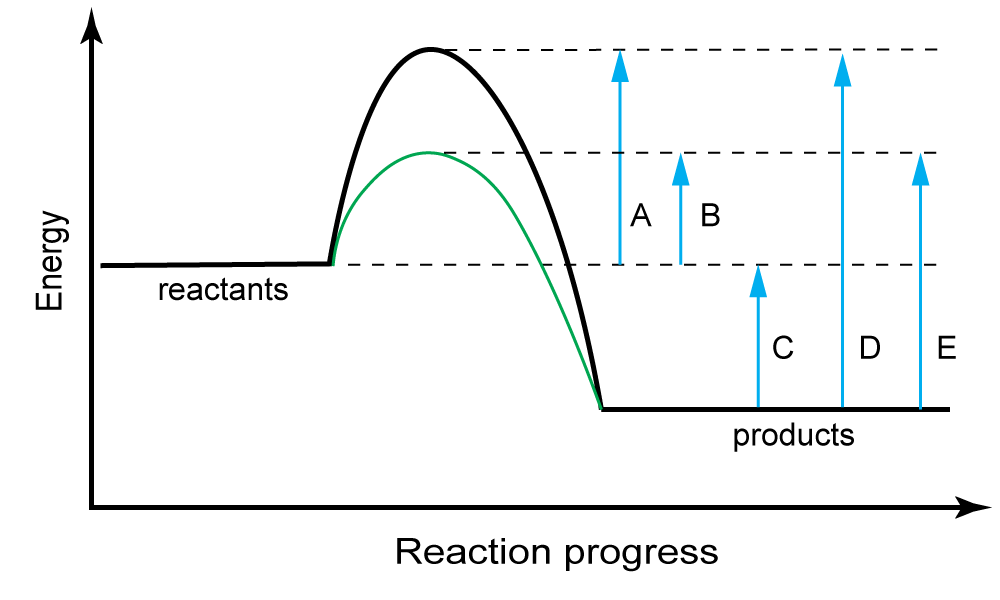
What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction . Describe the similarities and differences between the. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. A catalyst is a chemical substance. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis. a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction? a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically.
from gradegorilla.com
a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself. The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. Describe the similarities and differences between the. A catalyst is a chemical substance. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction?
Gradegorilla Chemistry
What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction? catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. Describe the similarities and differences between the. A catalyst is a chemical substance. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis.
From kierra-has-mercer.blogspot.com
What Happens to a Catalyst in a Reaction Apex KierrahasMercer What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT RATES OF REACTION A guide for GCSE students PowerPoint What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. Describe the similarities and differences between the. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Catalyst Reaction Diagram What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Describe the similarities and differences between the. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. a catalyst is a substance that. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From 2012books.lardbucket.org
Catalysis What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. a. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.pinterest.com
Catalyst Easy Science Energy activities, Chemical reactions What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction A catalyst is a chemical substance. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction? The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. a catalyst binds to a reactant and. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From circuitdiagramlows.z22.web.core.windows.net
Catalyst Energy Diagram What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
Enzymes Properties and Mechanism of enzyme action Online Biology Notes What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. A catalyst is a chemical substance. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis. what are catalysts, and how do they work in. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.slideshare.net
Biology 2.4 What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. A catalyst is a chemical substance.. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.youtube.com
Identifying catalysts in a reaction YouTube What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. catalysis is the process that alters the rate. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From derekcarrsavvy-chemist.blogspot.com
savvychemist GCSE OCR Gateway Chemistry C5.2 fi Catalysis and catalysts What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction? a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From fity.club
Enzyme The Catalyst What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. what are catalysts, and how do they work in. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CATALYSIS AND CATALYTIC REACTION MECHANISM PART 1 PowerPoint What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. what are catalysts, and how do they work in terms altering the parameters of a reaction? Catalysts can be homogenous. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From schoolbag.info
A catalyst speeds up a reaction by providing the reactants with an What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction When the catalyst is an enzyme, the enzyme binds to a substrate, leading to catalysis. The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.chemistrystudent.com
Catalysts (ALevel) ChemistryStudent What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. A catalyst is a chemical substance. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.youtube.com
A Catalyst and the Rate of Reaction YouTube What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction a catalyst binds to a reactant and it increases the number of collision between the reactant molecules, making the reaction more favorable thermodynamically. The rate and rate constant k of a reaction are. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. When the catalyst is an enzyme, the. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From celimoko.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Reactions Examples at Jenny McNear blog What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same. a catalyst binds to a reactant and it. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From www.expii.com
Catalysts (Enzymes) — Overview & Examples Expii What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction a catalyst changes the activation energy, e a, of a reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction. catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. A catalyst. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.
From exobghamq.blob.core.windows.net
Catalysts Chemical Equation at Joy Perry blog What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Describe the similarities and differences between the. catalysis is the process that alters the rate of a chemical reaction under the influence of a catalyst. a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the. What Happens To Catalysts During A Reaction.